当谈到自动驾驶,特斯拉的"纯视觉"方案通常占据头条。这种以视觉感知为主的技术路线,试图通过深度学习算法分析车载摄像头采集的影像,实现对车辆周围环境的感知和理解。然而,Wayve公司的研究团队却另辟蹊径,将语言交互引入自动驾驶系统。他们的最新成果LINGO-2,让智能汽车不仅能听懂驾驶员的口头指令,还能用自然语言解释自身决策。这一突破性进展为无人驾驶开启了全新的可能性。

LINGO-2正在重新定义自动驾驶?
LINGO-2并非要取代视觉感知,而是与其形成互补。通过语言指令优化决策过程,LINGO-2能够提升自动驾驶系统应对复杂场景的能力。举例来说,当遇到恶劣天气或道路施工等特殊情况时,驾驶员可以通过语音提示车辆采取应对措施。而LINGO-2则会根据指令和自身感知,给出恰当的反应并作出解释。这种人机协同不仅增强了自动驾驶的安全性,也让决策过程更加透明。
可以说,LINGO-2代表了自动驾驶技术的一种"另类"革命。它探索了人工智能在认知和交互层面的新边界,丰富了无人驾驶的实现路径。未来,视觉感知与语言交互势必会深度融合。
17 April 2024|Research
LINGO-2:Driving with Natural Language
This blog introduces LINGO-2,a driving model that links vision,language,and action to explain and determine driving behavior,opening up a new dimension of control and customization for an autonomous driving experience.LINGO-2 is the first closed-loop vision-language-action driving model(VLAM)tested on public roads.

Driving with Natural Language
In September 2023,we introduced natural language for autonomous driving in our blog on LINGO-1,an open-loop driving commentator that was a first step towards trustworthy autonomous driving technology.In November 2023,we further improved the accuracy and trustworthiness of LINGO-1’s responses by adding a“show and tell”capability through referential segmentation.Today,we are excited to present the next step in Wayve’s pioneering work incorporating natural language to enhance our driving models:introducing LINGO-2,a closed-loop vision-language-action driving model(VLAM)that is the first driving model trained on language tested on public roads.In this blog post,we share the technical details of our approach and examples of LINGO-2’s capability to combine language and action to accelerate the safe development of Wayve’s AI driving models.
2023年9月,我们在介绍LINGO-1的博客中首次提出了在自动驾驶中应用自然语言的概念。LINGO-1是一个开环(open-loop)驾驶评论系统,朝着实现值得信赖的自动驾驶技术迈出了第一步。2023年11月,我们通过增加"边显示边讲述"的参考分割功能,进一步提高了LINGO-1响应的准确性和可信度。今天,我们很高兴地介绍Wayve公司在将自然语言融入驾驶模型方面取得的新进展:LINGO-2,这是一个闭环(closed-loop)视觉-语言-行动驾驶模型,简称VLAM(Vision-Language-Action Model)。它是全球首个在公共道路上进行测试的、基于语言训练的驾驶模型。在这篇博文中,我们将分享LINGO-2的技术细节,并通过示例展示它如何将语言和行动结合起来,加速Wayve的AI驾驶模型的安全开发。
Introducing LINGO-2,a closed-loop Vision-Language-Action-Model(VLAM)
LINGO-2:一个闭环的视觉-语言-行动模型
Our previous model,LINGO-1,was an open-loop driving commentator that leveraged vision-language inputs to perform visual question answering(VQA)and driving commentary on tasks such as describing scene understanding,reasoning,and attention—providing only language as an output.This research model was an important first step in using language to understand what the model comprehends about the driving scene.LINGO-2 takes that one step further,providing visibility into the decision-making process of a driving model.
我们之前的模型LINGO-1是一个开环的驾驶评论系统。它利用视觉和语言输入来执行视觉问答(Visual Question Answering,VQA),对驾驶场景进行描述、推理和关注点分析,但只能生成语言输出。这个研究模型是我们在利用语言来理解驾驶模型对场景理解的重要一步。而LINGO-2则更进一步,它能让我们深入了解驾驶模型的决策过程。
LINGO-2 combines vision and language as inputs and outputs,both driving action and language,to provide a continuous driving commentary of its motion planning decisions.LINGO-2 adapts its actions and explanations in accordance with various scene elements and is a strong first indication of the alignment between explanations and decision-making.By linking language and action directly,LINGO-2 sheds light on how AI systems make decisions and opens up a new level of control and customization for driving.
LINGO-2同时将视觉和语言作为输入和输出,在输出驾驶动作的同时,还能生成对驾驶决策的实时解释。它可以根据不同的场景元素来调整驾驶行为和解释内容,初步证明了模型的解释与决策之间的高度一致性。通过直接关联语言和行动,LINGO-2揭示了AI系统的决策机制,为实现可控、个性化的驾驶体验开辟了新的可能。
While LINGO-1 could retrospectively generate commentary on driving scenarios,its commentary was not integrated with the driving model.Therefore,its observations were not informed by actual driving decisions.However,LINGO-2 can both generate real-time driving commentary and control a car.The linking of these fundamental modalities underscores the model’s profound understanding of the contextual semantics of the situation,for example,explaining that it’s slowing down for pedestrians on the road or executing an overtaking maneuver.It’s a crucial step towards enhancing trust in our assisted and autonomous driving systems.
尽管LINGO-1能够对驾驶场景进行事后评论,但它的评论与驾驶模型是分离的,并不是基于实际的驾驶决策。而LINGO-2不仅能生成实时驾驶解说,还能直接控制汽车的行驶。将这两个关键能力结合起来,凸显了LINGO-2对场景语义有着深刻的理解。例如,它能解释减速是因为前方有行人,或者说明正在执行超车动作。这是我们在提高用户对辅助驾驶和自动驾驶系统信任度方面迈出的关键一步。
It opens up new possibilities for accelerating learning with natural language by incorporating a description of driving actions and causal reasoning into the model’s training.Natural language interfaces could,even in the future,allow users to engage in conversations with the driving model,making it easier for people to understand these systems and build trust.
通过将驾驶动作和因果推理的描述纳入模型训练,LINGO-2为加速自然语言学习开辟了新的可能性。未来,自然语言交互界面甚至可以让用户与驾驶模型直接对话,让大众更容易理解和信任这些智能驾驶系统。
LINGO-2 Architecture:Multi-modal Transformer for Driving
LINGO-2架构:用于驾驶的多模态Transformer网络
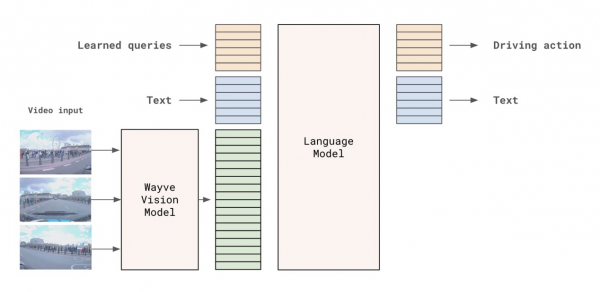
用于驾驶的多模态Transformer网络
LINGO-2 architecture
LINGO-2 consists of two modules:the Wayve vision model and the auto-regressive language model.The vision model processes camera images of consecutive timestamps into a sequence of tokens.These tokens and additional conditioning variables–such as route,current speed,and speed limit–are fed into the language model.Equipped with these inputs,the language model is trained to predict a driving trajectory and commentary text.Then,the car’s controller executes the driving trajectory.
LINGO-2包含两个主要模块:Wayve视觉模型和自回归语言模型。视觉模型将连续多帧相机图像转化为一系列tokens(可以理解为视觉特征)。这些tokens与其他控制变量(如路线、当前速度和限速等)一起输入到语言模型中。语言模型基于这些输入,学习预测驾驶轨迹和生成相应的解释文本。最后,汽车控制器负责执行规划好的驾驶轨迹。
LINGO-2’s New Capabilities
The integration of language and driving opens up new capabilities for autonomous driving and human-vehicle interaction,including:
1.Adapting driving behavior through language prompts:We can prompt LINGO-2 with constrained navigation commands(e.g.,“pull over,”“turn right,”etc.)and adapt the vehicle’s behavior.This has the potential to aid model training or,in some cases,enhance human-vehicle interaction.
2.Interrogating the AI model in real-time:LINGO-2 can predict and respond to questions about the scene and its decisions while driving.
3.Capturing real-time driving commentary:By linking vision,language,and action,LINGO-2 can leverage language to explain what it’s doing and why,shedding light on the AI’s decision-making process.
LINGO-2的新功能
将语言与驾驶控制结合,为自动驾驶和人机交互带来了诸多新的可能性,例如:
1.通过语言指令调整驾驶行为:我们可以用一些特定的导航命令(如"靠边停车"、"右转"等)来指示LINGO-2,从而改变车辆行驶方式。这有助于优化模型训练,在某些情况下还能提升人车交互体验。
2.实时询问AI模型:驾驶过程中,LINGO-2能够根据提问预测并回答与场景理解和决策相关的问题。
3.获取实时驾驶解说:通过关联视觉、语言和行动,LINGO-2能利用语言解释它当前的驾驶行为以及背后的原因,让我们更清楚地了解AI的决策过程。
We’ll explore these use cases in the sections below,showing examples of how we’ve tested LINGO-2 in our neural simulator Ghost Gym.Ghost Gym creates photorealistic 4D worlds for training,testing,and debugging our end-to-end AI driving models.Given the speed and complexity of real-world driving,we leverage offline simulation tools like Ghost Gym to evaluate the robustness of LINGO-2’s features first.
In this setup,LINGO-2 can freely navigate through an ever-changing synthetic environment,where we can run our model against the same scenarios with different language instructions and observe how it adapts its behavior.We can gain deep insights and rigorously test how the model behaves in complex driving scenarios,communicates its actions,and responds to linguistic instructions.
接下来,我们将通过在虚拟仿真环境Ghost Gym中测试LINGO-2的几个案例,来进一步探讨这些功能的应用。Ghost Gym是一个逼真的4D虚拟世界,用于端到端AI驾驶模型的训练、测试和调试。考虑到真实世界驾驶的高速性和复杂性,我们首先利用Ghost Gym这样的离线仿真工具来评估LINGO-2的性能和稳定性。
在Ghost Gym中,LINGO-2可以在不断变化的虚拟场景中自由导航。我们可以让模型在同一场景下执行不同的语言指令,观察它如何相应地调整驾驶行为。这使我们能够深入分析模型在复杂驾驶场景下的决策机制,了解它如何描述自己的行动,以及它对语言指令的响应能力。
Adapting Driving Behavior through Linguistic Instructions
通过语言指令调整驾驶行为
LINGO-2 uniquely allows driving instruction through natural language.To do this,we swap the order of text tokens and driving action,which means language becomes a prompt for the driving behavior.This section demonstrates the model’s ability to change its behavior in our neural simulator in response to language prompts for training purposes.This new capability opens up a new dimension of control and customization.The user can give commands or suggest alternative actions to the model.This is of particular value for training our AI and offers promise to enhance human-vehicle interaction for applications related to advanced driver assistance systems.In the examples below,we observe the same scenes repeated,with LINGO-2 adapting its behavior to follow linguistic instructions.
LINGO-2的一大特色是可以通过自然语言来指挥驾驶。为了实现这一点,我们调换了文本token(可以理解为词汇单元)和驾驶动作的顺序,使得语言指令成为驾驶行为的先导。本节将展示该模型在我们的虚拟仿真器中根据语言提示改变驾驶行为的能力,这对于模型训练大有裨益。这一全新功能为智能驾驶的控制和个性化开启了新的维度。用户可以向模型下达指令或建议替代动作。这不仅有利于优化我们的AI模型训练,还有望改善高级驾驶辅助系统中的人机交互体验。接下来,我们将通过一些示例来观察LINGO-2如何根据语言指令灵活调整驾驶行为。
Example 1:Navigating a junction
示例一:路口导航
In the three videos below,LINGO-2 navigates the same junction but is given different instructions:“turning left,clear road,”“turning right,clear road,”and“stopping at the give way line.”We observe that LINGO-2 can follow the instructions,reflected by different driving behaviors at the intersection.
在下面三个视频中,LINGO-2驾车通过同一个路口,但我们给出了三种不同的指令:"左转,道路通畅"、"右转,道路通畅"以及"在让行线处停车"。我们可以看到,LINGO-2能够遵照指令,在路口执行相应的驾驶动作。

Example of LINGO-2 driving in Ghost Gym and being prompted to turn left on a clear road.(视频:LINGO-2在Ghost Gym中根据提示"道路通畅,左转"执行左转)

Example of LINGO-2 driving in Ghost Gym and being prompted to turn right on a clear road.(视频:LINGO-2在Ghost Gym中根据提示"道路通畅,右转"执行右转)

Example of LINGO-2 driving in Ghost Gym and being prompted to stop at the give-way line.(视频:LINGO-2在Ghost Gym中根据提示"在让行线处停车"而停车)
Example 2:Navigating a bus
示例二:与公交车互动
In the two videos below,LINGO-2 navigates around a bus.We can observe that LINGO-2 can follow the instructions to either hold back and“stop behind the bus”or“accelerate and overtake the bus.”
接下来的两个视频展示了LINGO-2与公交车交互的场景。我们可以看到,LINGO-2能够根据"停在公交车后"或"超车并超越公交车"的指令采取相应的行动。
图片Example of LINGO-2 in Wayve’s Ghost Gym stopping behind the bus when instructed.(视频:LINGO-2在Wayve公司的Ghost Gym模拟器中根据指示停在公交车后方)
图片Example of LINGO-2 in Wayve’s Ghost Gym overtaking a bus when instructed by text.(视频:LINGO-2在Wayve公司的Ghost Gym模拟器中根据文字指令超越公交车)
Example 3:Driving in a residential area
示例三:住宅区驾驶
In the two videos below,LINGO-2 responds to linguistic instruction when driving in a residential area.It can correctly respond to the prompts“continue straight to follow the route”or“slow down for an upcoming turn.”
最后这两个视频展示了LINGO-2在住宅区道路上对语音指令的反应。它可以准确理解和执行"继续直行,沿路线行驶"或"减速,准备转弯"等命令。

Example of LINGO-2 in Wayve’s Ghost Gym driving straight when instructed bytext.(视频:LINGO-2在Ghost Gym中根据文字指令保持直线行驶)

Example of LINGO-2 in Wayve’s Ghost Gym turning right when instructed by text.(视频:LINGO-2在Ghost Gym中根据文字指令向右转弯)
Interrogating an AI model in real-time:Video Question Answering(VQA)
实时问询AI模型:视频问答(VQA)功能
Another possibility for language is to develop a layer of interaction between the robot car and the user that can give confidence in the decision-making capability of the driving model.Unlike our previous LINGO-1 research model,which could only answer questions retrospectively and was not directly connected to decision-making,LINGO-2 allows us to interrogate and prompt the actual model that is driving.
语言交互的另一个应用是在无人驾驶汽车和乘客之间建立一个对话界面,增强乘客对车辆决策能力的信心。不同于此前的LINGO-1研究模型只能事后回答问题,且与决策过程无直接关联,LINGO-2允许我们实时询问和指示当前行驶中的模型。
Example 4:Traffic Lights
示例四:交通信号灯
In this example,we show LINGO-2 driving through an intersection.When we ask the model,“What is the color of the traffic lights?”it correctly responds,“The traffic lights are green.”
这个例子中,LINGO-2驾车通过一个路口。当我们问模型"交通信号灯是什么颜色?"时,它正确回答:"交通信号灯是绿色。"

LINGO-2演示视频问答功能
Example of LINGO-2 VQA in Ghost Gym(视频:LINGO-2在Ghost Gym中演示视频问答功能)
Example 5:Hazard Identification
示例五:危险识别
In this example,LINGO-2 is prompted by the question,“Are there any hazards ahead of you?”It correctly identifies that“Yes,there is a cyclist ahead of me,which is why I am decelerating.”
在这个场景中,我们问LINGO-2:"前方有潜在危险吗?"它正确指出:"是的,前方有一名骑自行车者,所以我在减速。"
图片Example of LINGO-2 VQA in Ghost Gym(视频:LINGO-2在Ghost Gym中演示视频问答功能)
Example 6:Weather
示例六:天气情况
In the following three examples,we ask LINGO-2 to describe“What is the weather like?”It can correctly identify that the weather ranges from“very cloudy,there is no sign of the sun”to“sunny”to“the weather is clear with a blue sky and scattered clouds.”
接下来的三个片段中,我们让LINGO-2回答"现在天气如何?"。它分别给出了"乌云密布,看不到太阳"、"天气晴朗"和"晴空万里,偶有浮云"的恰当描述。
Example of LINGO-2 VQA in Ghost Gym(视频:LINGO-2在Ghost Gym中演示视频问答功能)
Limitations
目前的局限性
LINGO-2 marks a step-change in our progress to leverage natural language to enhance our AI driving models.While we are excited about the progress we are making,we also want to describe the current limitations of the model.
LINGO-2标志着我们在利用自然语言优化AI驾驶模型方面取得了突破性进展。尽管如此,我们也意识到该模型目前还存在一些局限性。
Language explanations from the driving model give us a strong idea of what the model might be thinking.However,more work is needed to quantify the alignment between explanations and decision-making.Future work will quantify and strengthen the connection between language,vision,and driving to reliably debug and explain model decisions.We expect to show in the real world that adding intermediate language reasoning in“chain-of-thought”driving helps solve edge cases and counterfactuals.
从模型给出的语言解释,我们可以大致了解其决策依据。但要准确衡量解释与决策的吻合程度,还需要做更多工作。未来,我们将着力量化语言、视觉、驾驶三者之间的关联,增强模型决策的可解释性和可靠性。我们希望通过实车测试证明,在"思维链"驾驶中融入语言推理有助于应对极端和反事实场景。
Additionally,we plan to investigate whether controlling the car’s behavior with language in real-world settings can be done reliably and safely.Ghost Gym provides a safe off-road environment for testing,but more work needs to be done to ensure the model is robust to noise and misinterpretation of the commands.It should understand the context of human instructions while never violating appropriate limits of safe and responsible driving behavior.This functionality will be more suited to aid model testing and training for fully automated driving systems.
此外,我们还将探索如何在真实道路环境中让语言安全、可靠地指挥车辆行驶。Ghost Gym提供了一个安全的虚拟测试空间,但要确保模型能正确理解口语化的指令且不受噪音干扰,还需要投入更多精力。模型必须能够准确把握人类指令的意图,同时严格遵守安全驾驶的基本原则。这一功能更适合应用于全自动驾驶系统的模型测试和训练。
Conclusion
In this post,we have introduced LINGO-2,the first driving model trained on language that has driven on public roads.We are excited to showcase how LINGO-2 can respond to language instruction and explain its driving actions in real-time.This is a first step towards building embodied AI that can perform multiple tasks,starting with language and driving.
结语
本文介绍了LINGO-2,这是首个接受语言指令训练并在公开道路上测试的驾驶模型。令人振奋的是,LINGO-2能够对语言提示作出实时反应,并对驾驶决策给出清晰解释。这为我们构建多功能智能体迈出了关键的一步。
Wayve是一家位于英国的自动驾驶技术初创公司,成立于2017年。与许多其他自动驾驶公司不同,Wayve的核心理念是通过端到端深度学习,让人工智能系统像人类一样学习驾驶技能。
以下是Wayve的一些关键特点:
1.端到端学习:Wayve的自动驾驶系统直接将感知信息(如摄像头图像)映射到车辆控制指令,无需手工设计的中间步骤。这种端到端学习方法让系统能够自主发现最优的驾驶策略。
2.少量数据学习:与需要海量数据训练的传统方法相比,Wayve的AI系统能够从较少的数据中快速学习,更加灵活和适应性强。
3.模拟到现实:Wayve先在虚拟环境中训练AI模型,再将其迁移到真实世界的汽车上进行微调。这种"模拟到现实"的方法大大加快了开发进度。
4.多模态融合:除了视觉信息,Wayve还尝试将自然语言指令整合到自动驾驶决策中。LINGO项目就是探索语言交互在无人驾驶中的应用。
5.安全与伦理:Wayve高度重视自动驾驶的安全性和伦理问题,致力于打造可靠、透明、符合社会期望的无人车系统。
总的来说,Wayve代表了自动驾驶技术的一种创新思路。他们的研究成果有望加速自动驾驶的发展,为未来交通出行带来革命性变化。尽管目前还处于探索阶段,但Wayve的尝试无疑为无人驾驶领域注入了新的活力。